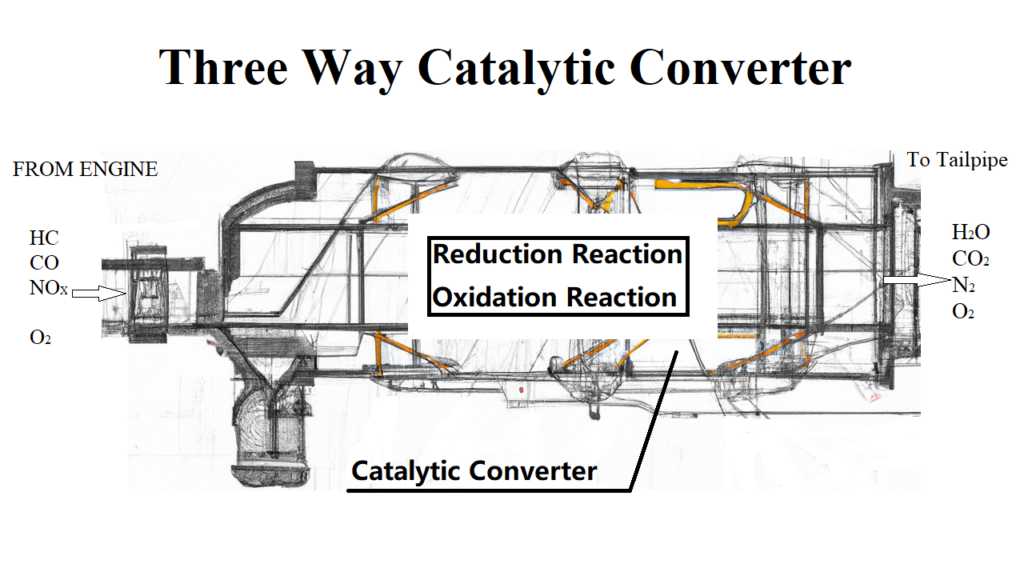
What is a Three Way Catalytic Converter?
The Three Way Catalytic Converter, also known as the TWC, is a device that has revolutionized the automotive industry. It was first developed in the 1970s as a way to reduce the harmful emissions that cars were producing, and it has since become an essential component of modern vehicles. In this article, we will explore the history and evolution of the Three Way Catalytic Converter, from its early days to its current state-of-the-art design.
The Beginning: The 1970s
In the 1970s, the world was becoming increasingly aware of the damaging effects of air pollution on the environment and human health. In response to these concerns, the United States government passed the Clean Air Act, which required car manufacturers to find ways to reduce emissions from their vehicles. It was around this time that the first Three Way Catalytic Converters were developed.
These early TWCs were relatively simple devices that consisted of a ceramic substrate coated with a mixture of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. When the exhaust gases from a car passed through the converter, the precious metals would catalyze a series of chemical reactions that would reduce the levels of harmful pollutants in the exhaust.
The 1980s and 1990s: Improving Efficiency
As the use of Three Way Catalytic Converters became more widespread, car manufacturers and researchers began looking for ways to improve their efficiency. One major area of focus was the catalytic substrate. In the 1980s and 1990s, new substrates were developed that were more durable and could better withstand the high temperatures and corrosive nature of the exhaust gases.
Another major development during this time was the use of computer-controlled engine management systems. These systems could precisely control the air/fuel mixture entering the engine, which allowed for more efficient operation of the TWC. This improved efficiency led to reduced emissions, improved fuel economy, and increased engine performance.
The 21st Century: Advances in Technology
In recent years, the Three Way Catalytic Converter has continued to evolve, thanks to advancements in materials science and computer technology. New catalytic substrates have been developed that are even more efficient and durable than those used in the past, while the use of sensors and computer control systems has allowed for more precise operation of the TWC.
One of the most notable developments in recent years has been the use of nano-scale precious metals in the catalytic substrate. These tiny particles are more active and efficient than the larger particles used in the past, which results in improved emission reduction. Additionally, the use of nano-scale precious metals has made the TWC more cost-effective, as less material is required to achieve the same results.
Conclusion
The Three Way Catalytic Converter has come a long way since its development in the 1970s. What was once a simple device has now become a highly sophisticated piece of technology, capable of reducing harmful emissions from cars to near-zero levels. As car manufacturers continue to search for ways to make vehicles more environmentally friendly, it is likely that the TWC will continue to evolve and improve in the years to come.